Abstract
Background: Marginal Zone Lymphomas (MZLs) are low-grade B cell lymphomas which include extranodal MZL (EMZL) of the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT), splenic MZL (SMZL), nodal MZL (NMZL). No definite consensus exists on treatment of MZL and although MZL generally shows an indolent course, high risk patients (pts), if early identified, might be intensively treated.
Aim of the study: The NF10 Project was started in 2010 by the Fondazione Italiana Linfomi as a prospective registry specifically conceived to investigate the prognosis of Indolent Non-Follicular B-Cell Lymphomas (INFL).We present an analysis of the registered MZLs, focusing on clinical aspects, pattern of care and outcome.
Methods: The registration of clinical, laboratory data along with treatment and outcome details of consecutive adult pts with newly diagnosed INFL is active at a dedicated website. All pts with a histologic confirmed diagnosis of INFL, including MZL, were eligible with no exclusion criteria. So far, the study has been activated in 65 centres in Europe and South America.
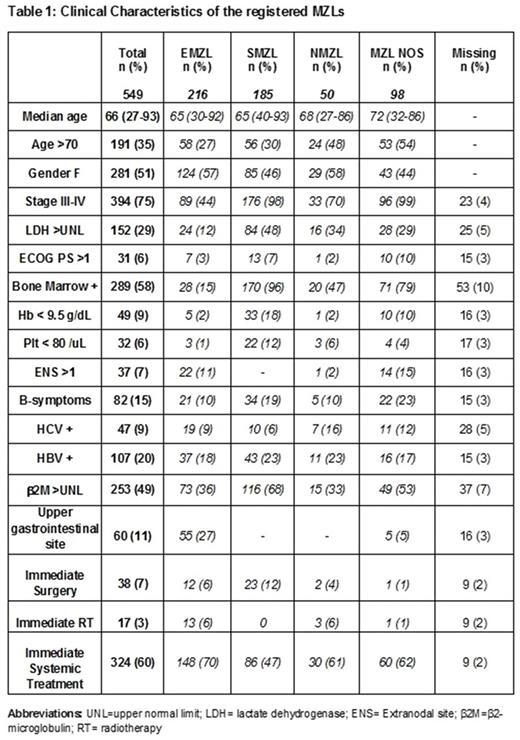
Results: Between July 2010 and July 2017, 1.044 INFL cases have been registered. MZLs were 549 (53%): 216 EMZL (39%), 185 SMZL (34%), 50 NMZL (9%); 98 cases were registered and classified as MZL Not Otherwise Specified (NOS 18%) based on the lack of a clear pattern of organ involvement. Median age was 66 years (range 27-93); Ann Arbor stage was III-IV in 75%; 15% had B symptoms, 6% had ECOG performance status (PS) >1, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and β2-microglobulin were > upper normal limit (UNL) in 29% and 49% of cases respectively; 9% had positive HCV serology and 20% positive HBV serology (17% HBcAb-positive and 3% HBsAg-positive). Bone marrow involvement was present in 58%; upper gastrointestinal site was involved in 55 EMZLs (27%). More than one extranodal sites (ENS>1) were involved in 37 cases (7%) (Table 1).
Regarding treatment, we observed a high heterogeneity in the treatment modalities across MZL subtypes and among pts subtypes within each MZL group. Immediate systemic treatment was planned in 324 pts (60%); in 149 pts addressed to observation, the median time to treatment (months) was 26.2 for MZL NOS, 15.5 for SMZL, 14.2 for NMZL and 5.1 for EMZL. The subtypes with the higher rates of immediate systemic therapy were EMZL, MZL NOS and NMZL (70%, 61%, 60% respectively). Bone marrow involvement (p<0.001), increased β2-microglobulin (p=0.006), ENS>1 (p=0.001) and HBV infection (p=0.009) were factors significantly associated with the need of immediate systemic treatment.
Rituximab (R) combined with chemotherapy was used in 248 (76%): R plus bendamustine (RB) in 114 (35%), R plus alkylating agents (R-alk) in 86 cases (27%) (mostly EMZL), R plus CHOP in 45 (14%) (mainly NMZL and MZL NOS); R monotherapy was used in 29 (9%). Since 2010 the use of RB has been increased from 9% to 40%. Conversely, the use of alkylating agents and/or CHOP decreased from 70% to 20%.
The median follow-up was 32 months (range 1-80). For treated pts 3y-PFS was 80% and 3y-OS was 89%; progressive disease was the cause of death in 33% of all cases. Overall, no difference was observed between RB and R-alk in terms of overall response rate (ORR), 3-year progression-free survival (3y-PFS), 3-year overall survival (3y-OS) and 3-year Failure-Free Survival (3y-FFS).
Among MZLs, IPI was able to identify a subgroup of 115 pts (24%) at high risk that showed a significantly shorter PFS and OS compared to intermediate and low risk subjects. Using subtype specific scores the HPLL (Montalbán et al, BJH 2012) for SMZL was able to identify 9 high risk pts (5%) with a 3y-PFS and 3y-OS of 35% and 48%, respectively. The recently published score for ENMZL generated from the dataset of the IELSG-19 clinical trial (Thieblemont et al, Blood 2017), was also considered for EMZL cases and was able to identify 29 (16%) high risk pts with a 3y-PFS and 3y-OS of 75% and 87%, respectively.
Conclusions: We provide an analysis of initial characteristics, treatment and outcome of a large series of pts with MZL. Despite the indolent course of MZL, a minority of pts with more aggressive clinical course is seen. Currently available scores suffer from a limited ability to identify a significant proportion of high risk pts who might be eligible to more intensive therapies. The NF10 Project with its relevant data collection deriving from a world-wide cooperation provides a solid base for future prognostic analysis and biological studies.
Re: Gilead: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Gaidano: Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria; Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria. Luminari: TAKEDA: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; TEVA: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; GILEAD: Speakers Bureau; PFIZER: Speakers Bureau; CELGENE: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; ROCHE: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Arcaini: Pfizer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Sandoz: Consultancy; Gilead: Research Funding; Roche: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bayer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal